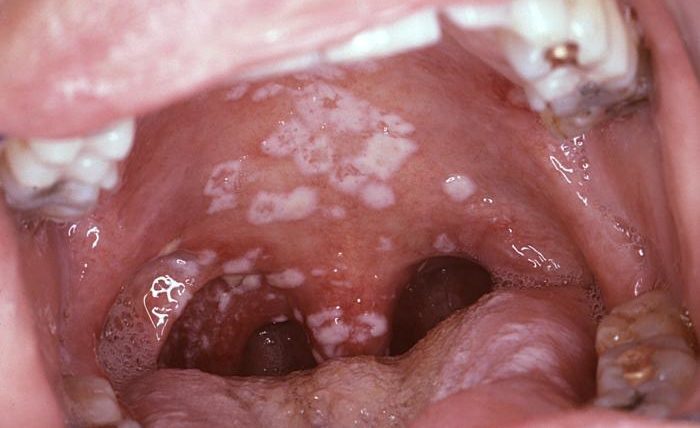
Chlamydia in the Throat: Chlamydia is bacterial and is caused by the chlamydia trachomatis strain. This strain thrives in vaginal fluid and semen. It can be passed on mainly through vaginal and anal sex. However, it can also be transmitted through oral sex. A Chlamydia oral infection is considered rare, however, you should realize that you are at a higher risk if you perform oral sex to a person who has never been tested for chlamydia and had more than one sex partner in the last 60 days.
Generally, chlamydia accounts for 250,000 to 500,000 cases of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women annually in the United States alone.
Female patients with chlamydia have about 5 times more chances of contracting HIV if exposed. Initial signs and symptoms of chlamydia are usually mild. They may cause painful urination, low fever and/or frequent urge to urinate.
Later symptoms can be more severe. They may cause fatigue, nausea and unusual discharge from the vagina in women and penis in men. Chlamydia in the throat, typically transmitted via oral sex, can lead to a sore throat and throat infection.
Other symptoms such as abdominal pain, irregular menstrual bleeding/spotting, lower back pain and pain during sex may follow if the chlamydia oral infection or other chlamydial infections are left untreated.
Do You Suspect Chlamydia in the Throat?
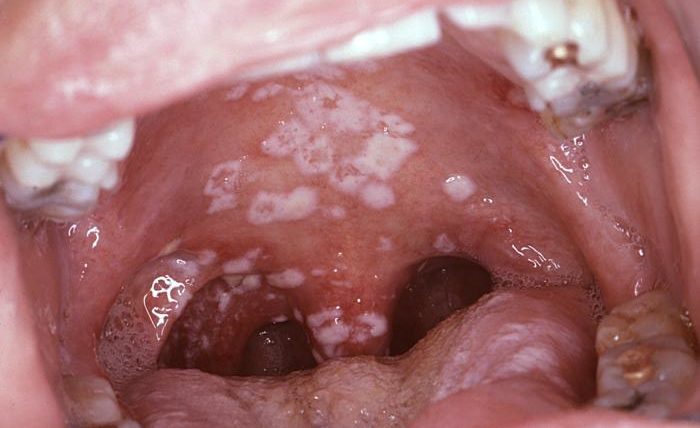 If you suspect you may have Chlamydia in the Throat, it would be a good idea to get tested right away. Think about how many times you’ve had sex and how many sex partners you’ve had recently.
If you suspect you may have Chlamydia in the Throat, it would be a good idea to get tested right away. Think about how many times you’ve had sex and how many sex partners you’ve had recently.
The more sex partners you’ve had the higher your risk of contracting chlamydia. Sexually active teens and young adults are found to have the highest risk.
Chlamydia oral infections can be so easily mistaken as a simple irritation of the throat, it is often left untreated.
In fact, chlamydia oral infections are found to be more frequently asymptomatic compared to chlamydia infections of the genitals. The surest way to prevent complications caused by untreated chlamydia is to get tested on a regular basis (i.e.: once a year).
The bacteria that cause chlamydia can affect any mucous membrane. A mucous membrane is any membrane that doesn’t have skin. This means that the throat and other areas inside the mouth can be easily infected. When an infection occurs in this case, it is known as a chlamydia oral infection. The fluid of an infected partner can infect your mucous membranes and transmit the disease to you.
A lot of sexual activity between two female sex partners or between two male sex partners comprises of oral sex. The chances of a homosexual in contracting a chlamydia oral infection is therefore higher. If you happen to have chlamydia pneumonia in your mouth, there’s a probability of transmitting chlamydia.
There’s a common misconception that oral sex automatically means “safer sex.” This is simply not true. Oral infections can carry the same bacteria. They ultimately lead to more serious complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease in women and swelling of the testicles in men. If you suspect you have a Chlamydia in the Throat, consult your doctor right away.