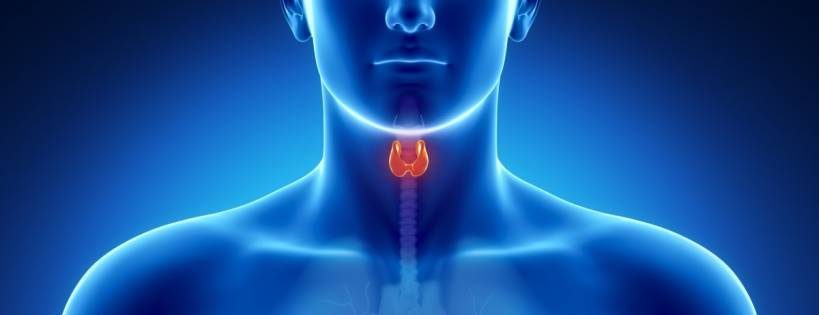
Thyroid Guide – Thyroid Disorders: The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped gland that can be found just below the Adam’s apple. It produces thyroid hormones that are used for metabolism in the body. The growth and development of all the body tissues are dependent on the proper functioning of the thyroid gland. Problems arise if the thyroid gland is overactive or underactive. There are three common thyroid disorders. These are hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism and the thyroid nodules.
Hypothyroidism happens when the thyroid gland fails to produce an adequate supply of thyroid hormones. Common symptoms of this thyroid disorder are hair loss, dry skin, sluggishness, constipation and weight gain.
Hyperthyroidism refers to an overactive thyroid gland. In this case, the thyroid gland produces more thyroid hormones than what the body needs. When this happens, an individual may feel exhausted most of the time, lose weight excessively, experience palpitations and irritability.
Order your At-Home Thyroid Test NOW! Results in 3 days!
Collect your sample, mail it back in the prepaid envelope, and receive results by email or phone.
Thyroid nodules are lumps that grow in the thyroid which are mostly common and harmless. Only a small percentage of thyroid nodules are cancerous. One must undergo a biopsy to be further evaluated if the lump or tumor is benign or cancerous.
Not all people with thyroid disorders may notice and feel symptoms. Someone can even go on living without having any clue that they may be suffering from a thyroid disorder. It is best to consult a doctor should an individual feel any symptoms either related or not related to thyroid disorders. Thyroid disorders if left untreated may put one’s health and even life at risk.
Interesting Questions about Thyroid:
The basic goal of treatment is to return thyroid hormone levels to normal.
Hyperthyroidism makes the body work too fast because there is too much thyroid hormone in the blood. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Graves’ disease occurs because of a problem in the body’s immune system: antibodies are produced that overstimulate the thyroid gland.
Patients who are hyperthyroid from taking too much thyroid hormone need only to have their dosage properly adjusted.
Patients whose hyperthyroidism is caused by transient thyroiditis usually do not require any of the treatments described below, since their condition gets better on its own.
Treatment for hyperthyroidism from Graves’ disease, toxic autonomously functioning thyroid nodule, or toxic multi-nodular goiter may include one or more of the following:
Radioactive iodine (I131)
Radioactive iodine shrinks an enlarged thyroid or toxic nodule or nodules that are making too much thyroid hormone. This treatment is safe and is widely used in adults with hyperthyroidism.
* Radioactive iodine (I131) is the treatment of choice for the majority of the endocrinologists in this country. It is an effective, simple, safe way to treat patients with Graves’ disease or other forms of hyperthyroidism. Patients often have fears and misconceptions about using radioactive iodine.
* Studies have been done since the 1940’s on patients receiving this treatment. Treated patients, their children, and their grandchildren do not have an increased incidence of cancer, leukemia, etc.
* There are no increased instances of birth defects in children born to mothers who have had this treatment and waited the recommended time before becoming pregnant. (Pregnancy should be avoided for at least six months after the treatment.) As a matter of fact, fertility is often restored to women whose infertility is due to hyperthyroidism. Treating the disease also lessens the chance of miscarriage.
* Pregnant women should not be given radioactive iodine for any reason. If a patient has any doubt as to whether she is pregnant, treatment (and testing) with radioactive iodine should be delayed.
* Hospitalization is not required in order to treat hyperthyroidism with radioactive iodine.
* Radioactive iodine treatment ablates the thyroid gland (turns it into something like a dried-up raisin). Patients wishing to avoid destruction of the gland should know that the thyroid gland frequently “burns out” within 15 years even without treatment.
* Radioactive iodine does not cause a person to gain weight. However, because Graves’ disease increases the metabolism, patients should keep in mind that they cannot continue to eat the way they did while hyperthyroid. Because of changes in the metabolism after hyperthyroidism is treated, many patients will gain weight . This weight can be lost through diet and exercise once the thyroid levels are normalized.
Antithyroid drugs
Propylthiouracil (PTU)
Tapazole®
Antithyroid drugs, such as propylthiouracil (PTU) and methimazole (Tapozole®), are used in patients with Graves’ disease and, less commonly, in other hyperthyroid patients
Surgery (thyroidectomy)
In some cases beta-blocking drugs are prescribed to treat the symptoms of hyperthyroidism while waiting for one of the above treatments to work.
Your doctor will be able to discuss the benefits and risks of each treatment.
Many patients treated for hyperthyroidism become hypothyroid. They will need to take thyroid hormone pills for the rest of their lives. In addition, they will need to see their doctor at least once a year.
® Tapozole is a registered trademark of Jones Medical Industries.
The standard treatment for hypothyroidism is thyroid hormone pills. The pills provide the body with the right amount of thyroid hormone when the gland is not able to produce enough by itself. While the symptoms of hypothyroidism are usually corrected within a few months, most patients need to take the pills for the rest of their lives.
The preferred thyroid hormone for treatment is levothyroxine (T4). You should use only the brand-name that your doctor prescribes, since generic brands may not be as reliable. Name brand levothyroxine pills include Levothroid®, Synthroid®, Levoxyl®, and Eltroxin®.
Patients sometimes take more pills than they should, trying to speed up the treatment or lose weight. However, this can lead to hyperthyroidism, a disease in which there is too much thyroid hormone in the blood, and to long-term complications, such as osteoporosis. You should take the pills as your doctor prescribes.
At different times in your life, you may need to take different amounts of thyroid hormones. Therefore, you should see your doctor once a year to make sure everything is all right.
® Levothroid is a registered trademark of Forest Pharmaceuticals.
® Synthroid is a registered trademark of Knoll Pharmaceuticals.
® Levoxyl is a registered trademark of Jones Medical Industries.
® Eltroxin is a registered trademark of Roberts Pharmaceuticals.
Signs and symptoms of Hyperthyroidism may include:
- fast heart rate (100-120 beats per minute or higher)
- slightly elevated blood pressure
- nervousness or irritability
- increased perspiration
- muscle weakness (especially in the shoulders, hips, and thighs)
- trembling hands
- weight loss, in spite of a good appetite
- hair loss
- fingernails partially separated from finger-tips (onycholysis)
- swollen fingertips (achropachy or clubbing)
- retracted (pulled back) upper eyelids
- skin changes
- increased frequency of bowel movements
- goiter (an abnormal swelling in the neck caused by an enlarged thyroid gland)
- in women, decreased menstrual flow and less frequent menstrual flow
- in men, slight swelling of the breasts
- in Graves’ disease: thick or swollen skin over the shin bones (pretibial myxedema); eyes that seem to be popping out of their socket (exophthalmos).
Most of these conditions will return to normal after the hyperthyroidism is treated. Certain others may be treated separately.
Have more questions? Need more answers? Check our Full Thyroid FAQ
Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders
Autoimmune thyroid disorders are common and occur when the thyroid gland is being attacked by the immune system. This results in an abnormal functioning of the thyroid gland. In cases like autoimmune thyroid disorders, the thyroid gland is either underactive or overactive. Examples of autoimmune thyroid disorders are Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Autoimmune thyroid disorders are also more common in women than in men. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis occurs in women between the ages of 30 and 50. This disease may be inherited since it appears to have a genetic component. People over 50 years old who have hypertension are prone to develop an autoimmune thyroid disorder called Graves’ disease.
Thyroid Disorder Symptoms
Thyroid disorder symptoms often appear gradually, thus making it commonly misdiagnosed. Some people may not feel or notice any symptoms at all. Common thyroid disorders are hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism and thyroid nodules. Common symptoms for hypothyroidism are weight gain, constipation, heavy or abnormal menstrual flows, dry skin and hair loss. As for hyperthyroidism, an individual may notice and experience hair loss, excessive weight loss, frequent bowel movement and irritability.
Thyroid nodules are often ignored because most of the time, the lumps or tumors are benign. But one must not ignore these lumps or tumors since these may also be cancerous. Should one feel any of these symptoms, it is best to consult a doctor and seek medical help. Tests will be done to check one’s thyroid function and determine if these symptoms are caused by any thyroid disorder.
Thyroid Guide & Links to Related Articles
Parathyroid |
There are four parathyroid glands that are normally having the size of a single rice grain. In some normal cases, they can be as big as the size of a pea. |
Hypothyroid |
Also called underactive thyroid, hypothyroidism is a disorder that is characterized by abnormal level of thyroid hormones in the body, which is too low. |
Thyroid Glands |
The thyroid is a butterfly (pear)-shaped gland, it consists of 2 symmetrical lobes joined by a central isthmus that normally covers the 2nd & 3rd tracheal rings. |
Congenital Hypothyroidism |
Congenital hypothyroidism is a thyroid gland disorder that may lead to deafness or mental retardation if left undetected. |
Thyroid Depression |
Hypothyroidism can cause depression. Most people don?t realize that this feeling is depression caused by the thyroid gland not functioning as it should. |
Papillary Thyroid Cancer |
Papillary thyroid cancer is one of the thyroid cancer types. This type of thyroid cancer arises from the follicles in the thyroid gland. |
Thyroid Gland Function |
The thyroid gland is located immediately below the larynx on each side of and anterior to the trachea. It is one of the largest of the endocrine glands |
Thyroid Hormone |
These thyroid hormones are responsible in regulating the body?s metabolism, which is how much food will be broken down into useful energy for consumption. |
Thyroid Levels |
When the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, one may suffer from hyperthyroidism. |
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone |
The thyroid stimulating hormone is produced by the pituitary gland. The thyroid stimulating hormone promotes the growth of the thyroid gland. |
Thyroid Hormones |
Thyroid hormones are chemical substances produced by the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck. |
Supplements for the Thyroid |
Natural thyroid supplements are helpful as a remedy to thyroid disorders. Its natural ingredients assure one of its safeties in taking it. |
Thyroid Symptoms in Women |
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland that is the primary responsible in regulating the body?s metabolism. |
Thyroid Surgery |
Thyroid surgery is used to treat people with thyroid problems such as thyroid cancer, thyroid nodules and hyperthyroidism. |
Thyroid Test |
Thyroid tests or thyroid function tests are done to check the thyroid function in one?s body. A doctor will be able to determine and diagnose the thyroid disorder. |
Thyroid Treatment |
Treatment for thyroid disorders should be done to prevent unwanted results caused by the severity of the condition. Consult a physician for more of these treatments. |
Thyroidectomy |
Thyroidectomy is a surgical process wherein the whole or a part of the thyroid gland is removed. This surgical process is used to treat thyroid disorders. |
Underactive Thyroid |
Having an underactive thyroid is a minor problem but it seeks proper attention to avoid further health problems. Consult a physician about any thyroid problem. |
Low Thyroid |
Low thyroid, also known as hypothyroidism, is a condition where the thyroid gland is under active. |
Under-Active Thyroid Diet |
Following a healthy meal plan, exercise and proper medication goes hand in hand to treat hypothyroidism. Consult a physician for a more individualized plan. |
Thyroid Cancer Treatment |
Each thyroid cancer treatment depends on the type of thyroid cancer and the extent or stage of the thyroid cancer one is suffering from. |
Parathyroid Hormone Levels |
Parathyroid hormones are considered to be the most important endocrine regulator. It basically regulates the calcium and phosphorus concentration in the body. |
Parathyroid Disease |
Studies show that since 1925, the standard treatment for parathyroid disease is to surgically remove the parathyroid gland(s) which are overproducing parathyroid hormones. |
Parathyroid Adenoma |
Parathyroid adenoma is a small tumor of the parathyroid gland and is known to be the most common disorder of the gland. |
Medullary Thyroid Cancer |
Medullary thyroid cancer is one of the types of thyroid cancer. This type of thyroid cancer is more common in women than in men. |
Overactive Thyroid |
Most people don?t feel any symptoms. Others can just lose weight and just feel depressed for no reason at all. |
Hypothyroidism |
Suppose you go in for a routine checkup and your doctor decides to test your thyroid function. You?ve experienced no thyroid disease symptoms |
Hypothyroidism Symptoms |
Hypothyroidism develops for over a long period of time. It?s normally from several months to even several years. |
Hypothyroidism Natural Treatment |
People who are suffering from hypothyroidism are advised to get plenty of exercise and have a balanced and healthy diet. The diet must be rich in protein and iodine. |
Hypothyroidism Diet |
Self medicating one?s thyroid disorder with hypothyroidism diet pills without proper information of the diet pill does not address the problem. |
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms & Treatment |
Hyperthyroidism is when the thyroid gland is overactive and produces too much thyroid hormones more than the body needs. |
Hypothyroidism |
Hypothyroidism is one of the chronic diseases in the world. Hypothyroidism is also known as underactive thyroid; hypo means under or below normal. |
Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer |
Anaplastic thyroid cancer is a type of thyroid cancer that is rare and aggressive. It affects the thyroid gland and most especially its function. |
Thyroid Disorders |
Problems arise if the thyroid gland is overactive or underactive. There are three common thyroid disorders. These are hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism and the thyroid nodules. |
Thyroid Hair Loss |
Hair loss may happen for so many reasons but it is commonly associated to thyroid problems such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. |
Thyroid Function Test |
Thyroid Function Tests are the different tests conducted to assess and determine the cause of an individual?s thyroid problems. |